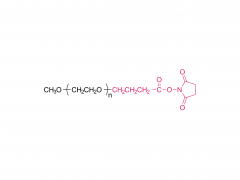
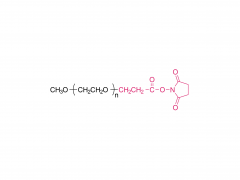
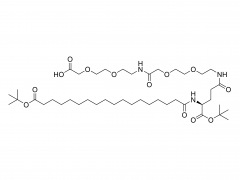
ポリエチレングリコール(PEG) は重要な合成ポリマーとして、優れた生体適合性、低毒性、優れた溶解性により、医薬品やバイオメディシンで広く使用されています。近年、ポリエチレングリコールの多分岐型(多分岐PEG)は、そのユニークな構造特性により、薬物送達やバイオエンジニアリングにおいて不可欠な材料となっています。その多様な用途は、医薬品製剤の有効性を高めるだけでなく、バイオ医薬品における革新の新たな道筋を提供します
-
多分岐ポリエチレングリコールの基本特性
マルチアームポリエチレングリコールとは、主PEG骨格に2つ以上のポリエチレングリコール側鎖が結合した分子を指します。このマルチアーム構造は、シングルアームPEGと比較して、より柔軟で強力な結合性を示し、生物学的応用において優れた特性を発揮します。マルチアームPEGのアーム数と分子量を調整することで、薬物放出速度を精密に制御することができ、様々な応用シナリオのニーズに対応します。 -
薬物送達におけるマルチアームポリエチレングリコールの応用
-
標的薬物キャリア
多腕ポリエチレングリコールは、薬物送達システムにおける標的薬物キャリアとして一般的に使用されています。多腕構造のため、薬物分子と安定な複合体を形成し、薬物の生物学的利用能を向上させます。この構造は特定の標的細胞に結合するように改変することができ、薬物の選択性を高め、健康な細胞への影響を最小限に抑えながら、標的部位へのより効果的な送達を可能にします -
徐放性製剤
徐放性製剤の開発において、多分岐ポリエチレングリコールは大きな利点を提供します。その独自の分子構造により、より安定したミセルまたはマイクロカプセルを形成し、薬物の放出時間を効果的に延長することができます。例えば、多分岐ポリエチレングリコールを用いて調製された徐放性製剤は、長期間にわたって薬物を持続的に放出することができ、慢性疾患患者の投薬ニーズを満たします -
生体材料
組織工学および生体材料における多腕ポリエチレングリコールの応用は拡大し続けています。多腕PEGを他の生体材料と組み合わせて複合スキャフォールドを形成することで、細胞の成長に適した環境を提供し、組織の修復を促進します。特に筋肉や骨の再生において、この構造を持つ材料は組織再生率を大幅に向上させ、患者により良いリハビリテーション体験を提供します -
ワクチン開発における多腕ポリエチレングリコールの役割
ワクチン研究の進歩に伴い、多鎖ポリエチレングリコールの応用がますます注目を集めています。その独特な構造特性を活用することで、ワクチンの免疫原性を高めることができます。抗原分子を多鎖PEGで修飾することで、ワクチンの安定性と有効性を効果的に向上させ、免疫システムの反応を強化できます。さらに、ナノキャリアワクチンへの多鎖ポリエチレングリコールの応用は、新規ワクチン開発の可能性をさらに広げます。 -
生産プロセスと技術的優位性
多分岐ポリエチレングリコールの製造プロセスは複雑で、高精度の重合および修飾工程が必要です。厦門賽諾邦格生物科技有限公司は、この分野で豊富な経験と技術を蓄積してきました。高度なCDMOモデルを導入することで、すべての製造工程が国際基準を満たしていることを保証しています。この効率的な生産能力は、医薬品開発を強力にサポートするだけでなく、顧客の研究開発コストの削減にも貢献し、製品の市場競争力を高めます。
マルチアーム型ポリエチレングリコールは、薬物送達、徐放性製剤、生体材料、ワクチン開発など幅広い分野で応用されており、その大きな可能性と柔軟性を実証しています。この高分子材料は、製薬業界に大きな革新をもたらしただけでなく、患者の生活の質の向上にも大きく貢献しています。製薬会社は、マルチアーム型ポリエチレングリコールの用途を継続的に探求することで、市場の需要に適切に対応し、バイオ医薬品技術を進歩させ、より高い治療効果を達成することができます。